In the relentless pursuit of sustainable energy, the advent of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) has marked a significant turning point. A recent breakthrough researched by a team at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) sheds light on the uncharted territory of chiral structures within these devices, showcasing an innovative way to dramatically improve their performance and commercial viability. The implications of this research could redefine not only how we harness solar energy but also the fundamental expectations surrounding its reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in everyday applications.
The Chiral Transformation
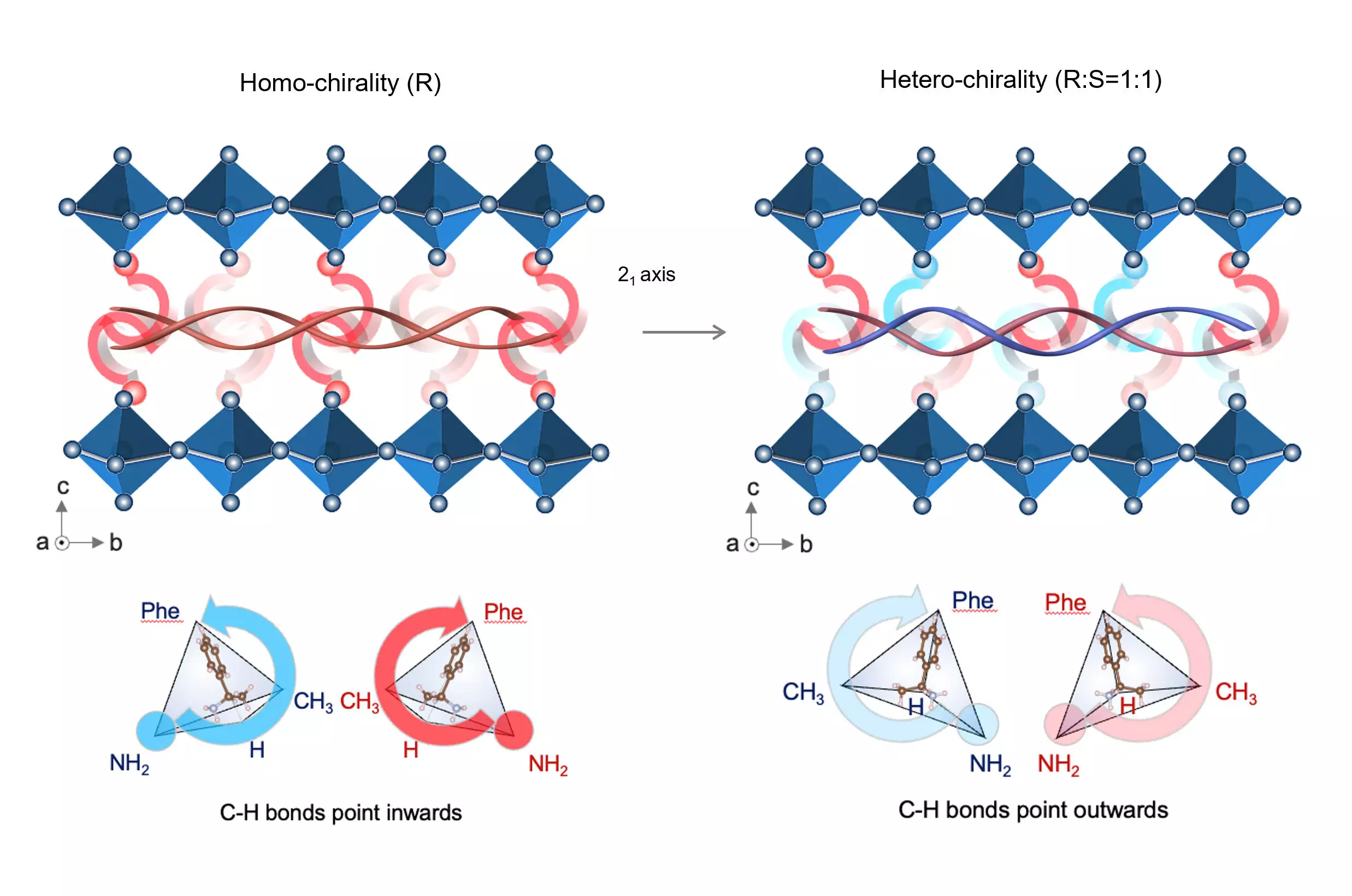
At the crux of the team’s discovery lies the innovative application of chiral-structured heterointerfaces. Chiral materials are renowned for their unique mechanical properties that stem from the helical arrangement of their constituent components. By integrating a chiral-structured interlayer crafted from R-/S-methylbenzyl-ammonium between the perovskite absorber and the electron transport layer, the researchers have created an interface that resembles a mechanical spring—offering both robustness and flexibility for the solar cells.
Chiral structures have been widely studied in nature, particularly in biological systems, where their propensity for resilience and adaptability is critical. This research, as detailed in their paper published in the journal Science, not only draws inspiration from nature but also exemplifies how such principles can be transliterated into technology. The durability of these solar cells is monumental, with the cells sustaining over 92% of their initial power conversion rates after extensive thermal cycling, validating their potential for real-world applications.
Challenges of Commercialization
Despite the impressive performance of PSCs, commercialization has encountered significant hurdles, primarily due to stability concerns. Conventional silicon-based solar cells, while historically reliable, involve expensive production processes and often lack the innovative edge that perovskites can offer. The inherent challenges of poor interfacial adhesion in PSCs, which previously curtailed their longevity and effectiveness, now appear surmountable through this ingenious approach.
Prof. Zhou Yuanyuan and the research team’s insight into the mechanics of chiral materials highlights a vital breakthrough that may catalyze the transition from laboratory experimentation to widespread deployment. As renewable energy sources face an ever-intensifying demand, such advancements become pivotal. This team’s work, thus, could significantly shorten the timeline for perovskites to be integrated extensively into the energy market.
Implications for Sustainable Energy
The implications of robust and reliable perovskite solar panels are undeniably profound. With enhanced durability across various environmental conditions, these solar panels could effectively provide sustainable energy in diverse geographic and climate settings. This breakthrough not only positions perovskite technology in a favorable light but also potentially paves the way for reduced overall energy costs as production techniques evolve and scale.
The potential for billions of dollars in the energy marketplace hinges upon resolving the reliability of PSCs. For countries striving to minimize their carbon footprint, investing in this technology could bolster energy independence and affordability. The marriage of high efficiency, affordability, and mass production could shift the paradigm in how the world exercises energy consumption.
The Road Ahead for Solar Energy
Prof. Zhou’s statement regarding the dawn of a new era for perovskite solar cells rings particularly true. The research embarked upon by the HKUST team illuminates a path forward that includes collaboration across international institutions, with contributions from notable facilities such as the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory and Yale University. Such collaborative efforts are essential, as they promise not just innovation within academic silos but the possibility for a unified approach to tackling global energy challenges.
As we steer towards a future increasingly reliant on renewable energy sources, this transformative research signifies not only a technical achievement but a reawakening in the energy sector. Perovskite solar cells could finally realize their true potential for extensive utilization, proving to be a cornerstone for a sustainable and environmentally friendly power landscape. The momentum generated by such breakthroughs can inspire future endeavors aimed at further optimizing renewable technologies, ensuring that we move forth into a greener era.

Leave a Reply