In the ever-evolving field of modern medicine, protein therapeutics have emerged as a beacon of hope for treating an array of serious health conditions, from diabetes to various cancers. These therapies rely on the delicate balance of proteins that require precise handling and storage, often demanding stringent temperature controls. The recent innovation developed by researchers from the Universities of Manchester, Glasgow, and Warwick, as published in *Nature*, presents a paradigm shift: a hydrogel designed not only to stabilize these proteins but also to facilitate their distribution in environments lacking proper cold storage facilities. This avant-garde approach could dramatically improve healthcare accessibility worldwide, particularly in developing nations.
The Challenge of Cold Chain Logistics
The traditional “cold chain” logistics system required for transporting protein therapeutics underscores a significant challenge in healthcare delivery. As medical professionals faced notable issues during the global rollout of COVID-19 vaccines—highlighting the difficulties associated with maintaining temperature thresholds—there arose a compelling need for alternatives. The standard requirement for refrigeration not only incurs high energy costs but also poses logistical nightmares, especially in areas where infrastructure is inadequate. The hydrogel innovation promises to dismantle these barriers, allowing for the transportation of protein therapeutics even in extreme conditions.
Understanding the Hydrogel Mechanism
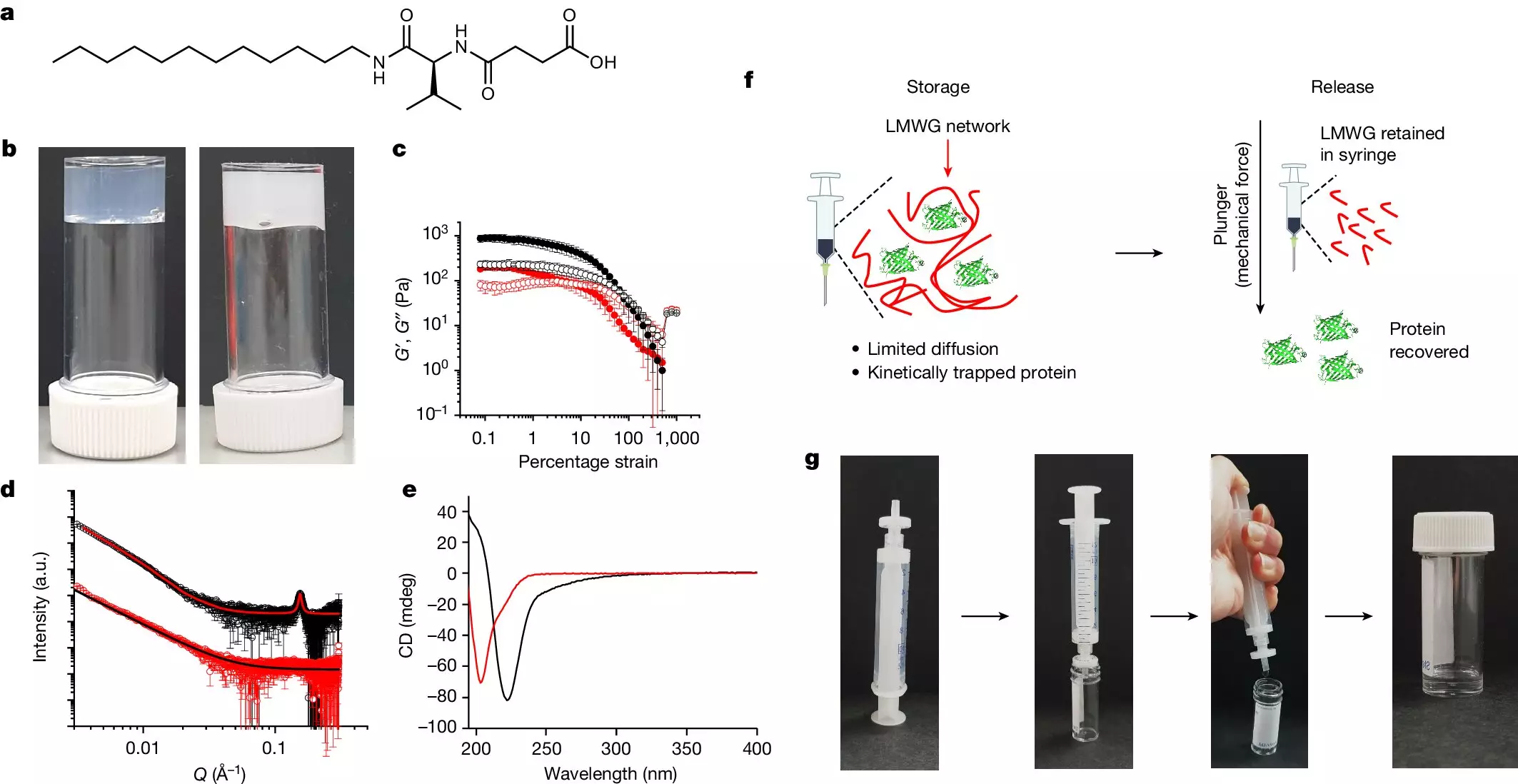
At the core of this technological advancement lies a low molecular weight gelator (LMWG), which forms a three-dimensional framework of stiff, resistant fibers. This structure entraps proteins in a protective environment, limiting their exposure to factors that typically lead to degradation. By preventing aggregation—an obstacle that diminishes therapeutic efficacy—the hydrogel offers an inventive solution that could redefine how protein-based drugs are stored and delivered. When pressure is applied through syringes fitted with a specialized filter, proteins are released safely, accompanying a buffer solution, ensuring that their functional properties are preserved.
Stability Tests: Pushing the Limits
The rigorous testing undertaken by the researchers showcases the robustness of this hydrogel. For instance, insulin, which must be meticulously maintained at lower temperatures to retain its potency, was subjected to conditions that would typically jeopardize its effectiveness. In a strain test involving high temperatures and rapid rotation, the hydrogel maintained the integrity of the insulin, allowing for a complete recovery of the drug after exposure. Similarly, beta-galactosidase, another critical enzyme, was stored at a scorching 50°C for a week and ultimately retained an impressive 97% of its functionality upon extraction. This not only demonstrates the impressive stability of the hydrogel but also offers a glimpse into a future where protein therapeutics are much less vulnerable to environmental stresses.
Potential Implications for Global Health
The implications of this breakthrough resonate far beyond the laboratory. In under-resourced regions, the absence of cold chain systems often means that life-saving treatments are simply out of reach. With the introduction of a temperature-stable hydrogel, communities could see an increase in the availability of vital protein-based drugs. This technology could well empower healthcare workers, making it easier to diagnose and treat conditions that previously posed staggering hurdles due to logistical constraints.
Commercial Viability and Future Directions
While the results are promising, the road to widespread commercial application lies ahead. The researchers are actively exploring commercial opportunities for this patent-pending technology. Addressing safety concerns—especially ensuring that the hydrogel does not interfere with the function or safety of the proteins—will be crucial in transitioning from laboratory success to public healthcare application. Nevertheless, the potential is vast, and the research team’s enthusiasm in revealing their findings suggests a commitment to realizing this vision.
The Vision Ahead: A New Era in Therapeutic Distribution
As society continues striving for equitable access to medical advancements, innovations like this hydrogel could serve as a critical tool in bridging the healthcare gap. By overcoming the limitations of the cold chain, this new technology not only augurs well for the future of protein therapeutics but also underscores a thoughtful, proactive approach toward healthcare equity on a global scale. In the quest for better health outcomes, every step that improves access to effective treatments is a noteworthy advance—one that this revolutionary hydrogel may very well catalyze.

Leave a Reply