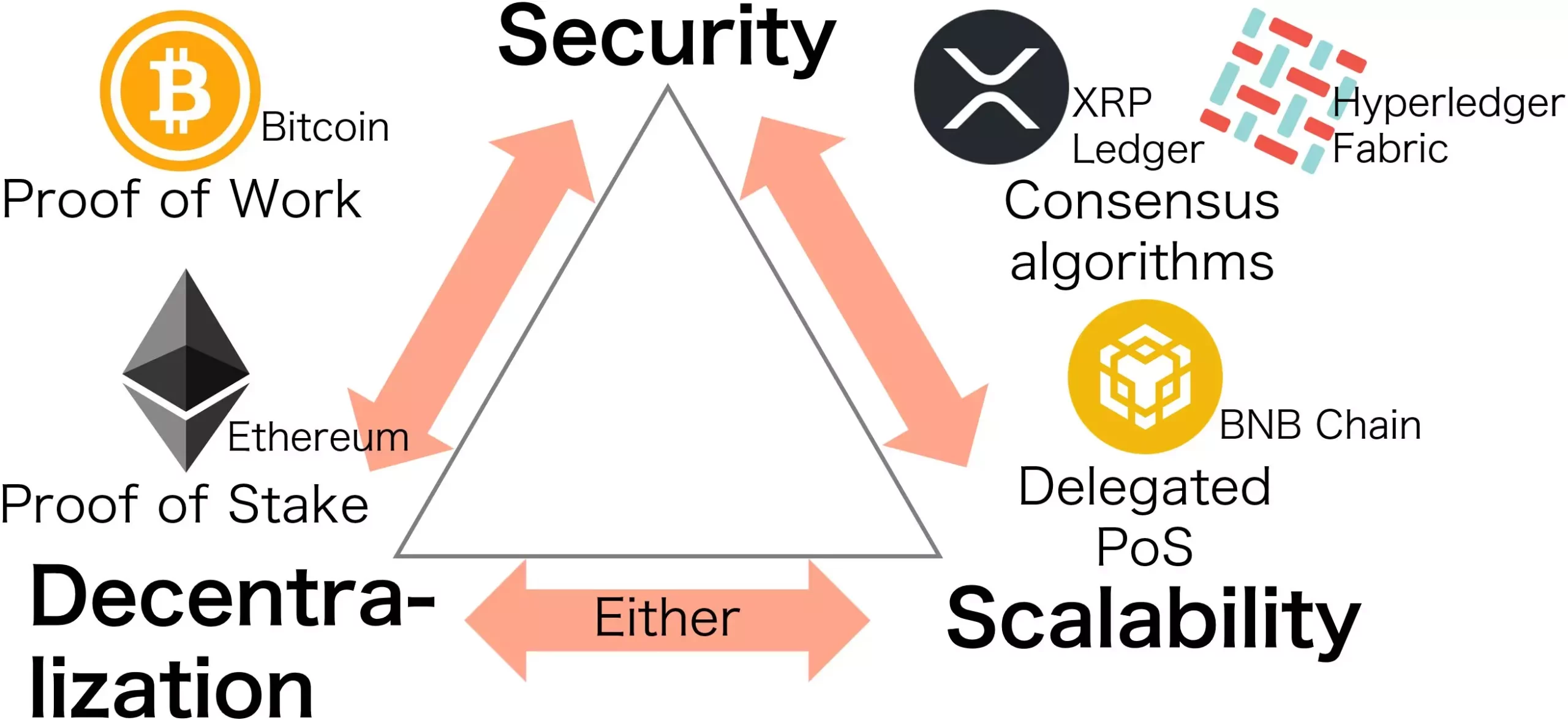
In the realm of blockchain technology, the pursuit of scalability, security, and decentralization often feels like a tug-of-war. Traditionally, it has been accepted that achieving all three is a near-impossible endeavor; this notion is succinctly encapsulated in the blockchain trilemma. The groundbreaking work from a team of researchers at Kyoto University now offers a fresh mathematical lens through which to view this conundrum. Their research articulates a formula that not only clarifies the interdependencies among these three crucial facets but also opens new avenues to enhance blockchain performance without compromising individual components.
Cracking the Code: A New Formula for Improvement
Led by Kazuyuki Shudo, this team has delved deeply into the mechanics behind Proof of Work-based systems such as Bitcoin. Their assertion is powerful: the cumulative product of scalability, security, and decentralization equals one. This elegant equation lays a foundation for emerging technologies to strive for improvements in scalability without the trade-off previously thought inevitable. Shudo notes that by reducing block sizes or expediting transaction times, developers can significantly enhance scalability within the existing framework of blockchain systems.
Consider Bitcoin’s Compact Block Relay as a concrete example, which strives to decrease transaction sizes while grappling with the very essence of blockchain’s foundational challenges. Such innovations underscore a critical realization: while increasing one aspect invariably leads to a decrease in another, clever engineering and mathematical insights might harmonize these elements better than previously thought conceivable.
The Confusion of Claims: Insights from the Blockchain Community
The discourse surrounding the trilemma is far from homogeneous. Influential figures, including Vitalik Buterin, have sparked debates with their interpretations, prompting diverse solutions that sometimes border on speculative. Many projects aimed at scalability have emerged, but they have often failed to provide clear evidence demonstrating their efficacy in maintaining security and decentralization. Shudo’s insights into this muddled landscape are particularly pertinent, as they illuminate the need for a thorough examination of existing methodologies that strive for improvement.
Moreover, the application of advanced mathematical tools, such as the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index, provides a measure of market decentralization concerning blockchain hash rates. By integrating concepts from previous research on blockchain security and transaction speed, Shudo’s team has forged novel connections that may inspire future breakthroughs in the field.
Acknowledging the Evolution of Blockchains
It’s important to remember that while Bitcoin and its Proof of Work method provide a significant case study, other systems like Ethereum, which has recently transitioned to Proof of Stake, are equally vital in this discussion. The evolution of blockchain technologies demands an acknowledgment of their unique challenges and strengths. The Kyoto University team’s commitment to understanding and enhancing these constructs illustrates a broader need for multidisciplinary approaches in blockchain research.
Their conclusion urges continued exploration beyond established paradigms, indicating that the future of blockchain might not reside solely in its foundational technologies but also in the ingenuity of mathematical modeling and computational analysis.

Leave a Reply