In today’s digital age, wireless internet has become an integral part of our daily lives, facilitating a wide range of activities from professional communications to entertainment. However, the growing demand for wireless internet access comes with a significant environmental cost in terms of power consumption and carbon emissions. Researchers are now focusing on developing energy-efficient solutions to support the high computational demands of modern applications and internet services. One such innovative approach is visible light communication (VLC), which utilizes light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or artificial light sources to transmit data wirelessly.
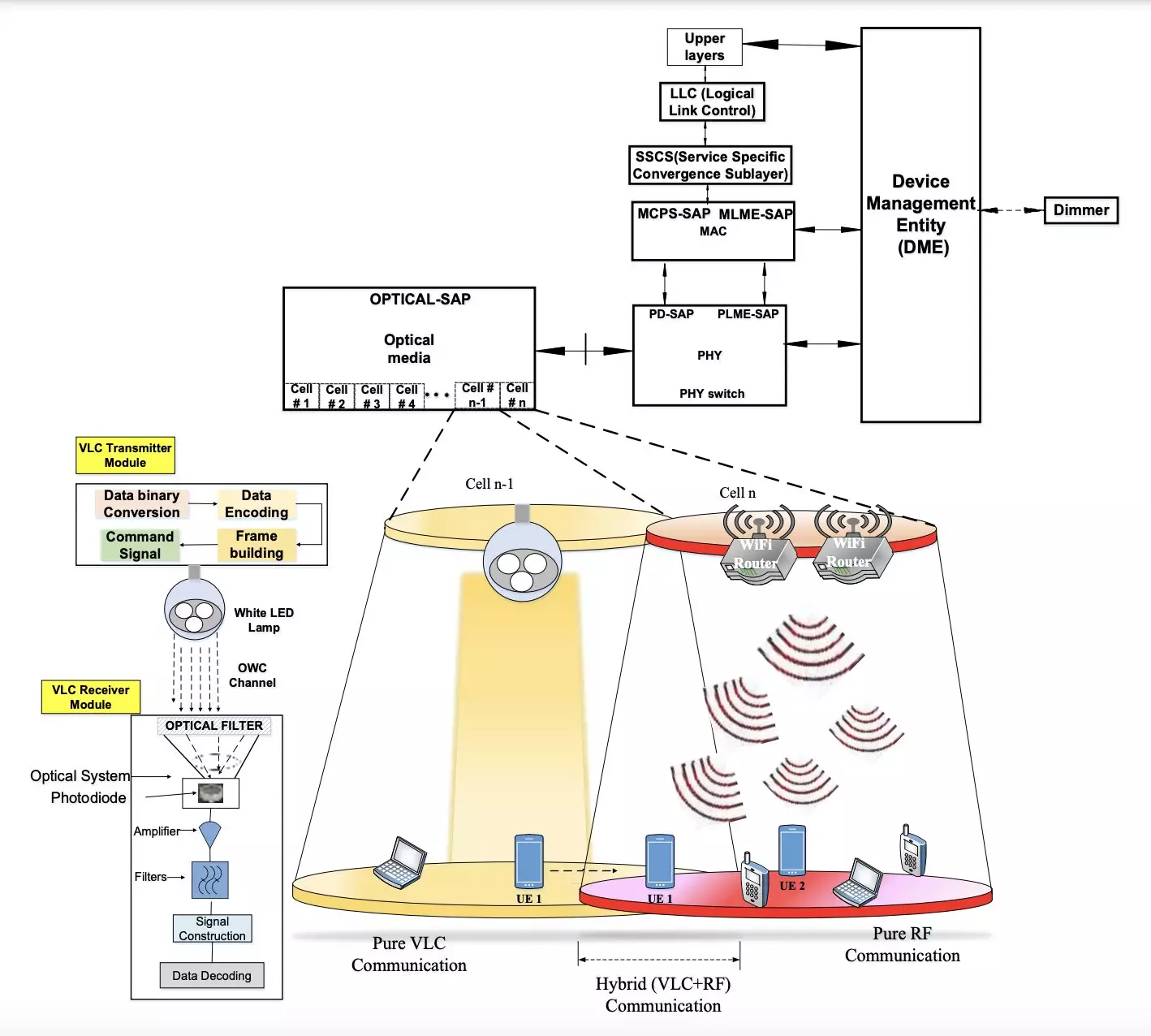
A recent study by researchers at Central University (CU), IIDM, and CU J&K in India introduces a novel hybrid approach that combines VLC with RF communication to enable reliable and energy-efficient indoor wireless communication. This hybrid system aims to provide high data transmission rates while minimizing power consumption, thus reducing the carbon footprint and enhancing network reliability. By merging the benefits of RF and VLC technologies, the researchers believe they can maintain the required Quality of Service (QoS) and Quality of Experience (QoE) for various applications.
The wireless communication system proposed by the research team consists of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver module. These modules operate independently but are connected through a VLC channel. The transmitter converts binary data into LED-produced light for transmission, while modulation schemes ensure a continuous data stream and constant energy consumption. On the other hand, the receiver includes a photosensitive device, such as a photodiode or camera, to extract information from the transmitted light. This setup enables stable communication between devices within the same indoor environment.
To evaluate the performance of their hybrid RF-VLC system, the researchers conducted simulations using Python, Scilab, and MathWorks tools. The results indicated significant energy savings compared to traditional RF communication, with improved energy efficiency and reduced electromagnetic radiation exposure. The proposed system achieved a low Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) and increased battery lifetime for mobile devices, demonstrating its potential for real-world applications. By enhancing communication stability and energy efficiency, the researchers aim to address the growing concerns related to power consumption and environmental impact.
The recent study by the research team represents a step forward in the development of energy-efficient wireless communication technologies. By combining VLC with RF communication, they have demonstrated the feasibility of reducing power consumption while maintaining reliable communication quality. Future studies will focus on further refining and testing the hybrid system to optimize its performance and applicability. Overall, the integration of VLC and RF technologies holds promise for enhancing wireless communication efficiency and sustainability in the digital era.

Leave a Reply